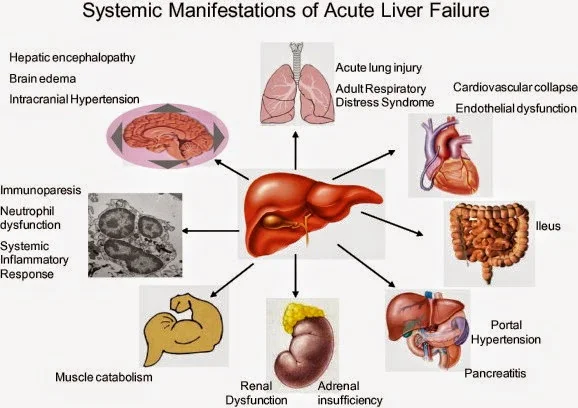
Signs and Symptoms
- Manifestation depends on the complications associated with the liver dysfunction.
- Patient behavior may range from agitation to frank coma.
- Evidence of GI bleeding, renal failure, or respiratory distress may also be present.
- The initial manifestation in FHF is commonly bleeding from coagulopathy.
Physical Examination
Vital signs- BP: < 90 mm Hg (with shock)
- HR: > 120 beats/min (with shock)
- Temperature may be mildly elevated
- RR: tachypnea initially progressing to respiratory depression associated with encephalopathy.
- Mildly confused to coma
- Personality changes
- Asterixis
- Crackles
- Labored respirations
- Hematemesis and melena
- Ascites
- Hepatomegaly may be present
- Splenomegaly may be present
- Factor hepaticus
- Diarrhea
- Jaundice
- Ecchymosis and petechiae
- Pruritus
- Edema
Acute Care Patient Management
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient fluid volume related to ascites secondary to hypoalbumineia, bleeding secondary to decreased clotting factors or variceal hemorrhage, and diuretic therapy.Outcome Criteria
- BP 90 TO 120 mm Hg
- Central venous pressure 2 to 6 mm Hg
- Serum albumin 3.5 to 5 mg/dl
- Platelet count >50,000/mm3
- Urine output 30 ml/hr
- Serum sodium 135 to 145 mEq/L
- Serum potassium 3.5 to 5 mEq/L
- Intake approximates output
- Obtain pulmonary artery pressure, central venous pressure, and blood pressure until the patient’s condition is stable, then hourly.
- Continuously monitor ECG for lethal dysrhythmias that may result from electrolyte and acid-base imbalances.
- Monitor fluid volume status. Measure intake and output hourly.
- Assess hydration status. Note skin turgor on inner thigh or forehead, condition of buccal memranes, and development of edema and crackles.
- Assess for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
- Measure abdominal girth once each shift to determine progression of ascites.
- Assess respiratory status.
- Review serial serum ammonia, albumin, bilirubin, platelet count, PT, PTT and ALT to evaluate hepatic function.
- Review serial serum electrolytes.
- Review urine electrolyte, BUN, and creatinine to evaluate renal function.
- Administer intravenous crystalloids as ordered.
- Administer potassium as ordered. Validate adequate urine output before potassium administration.
- Sodium restriction of 0.5 g/day and fluid restriction to 1000 ml/day may be ordered.
- Vitamin K or fresh frozen plasma (FFP) may be required to promote the clotting process.
- Institute bleeding precautions. Avoid razor blades and use soft-bristled toothbrushes.
- Paracentesis may be performed if abdominal distention is severe.
- Prepare the patient and family for liver transplant, as indicated.
No comments:
Post a Comment